Introduction to Optimizing Crane Durability Through Rigorous Protocols
Crane maintenance is vital In heavy machinery operations, overhead and gantry lifting systems demand disciplined upkeep to achieve maximum longevity. For instance, well-structured service plans can extend baseline endurance from 20-30 years to double that span. Moreover, this approach minimizes unexpected breakdowns and significantly reduces downtime expenses. This comprehensive guide delves into proven strategies for enhancing crane resilience. It integrates established engineering principles with mandatory regulatory frameworks. We examine structural integrity evaluations, hydraulic system management, electrical diagnostics, operator training protocols, and environmental adaptations. Consequently, implementing these measures allows organizations to prolong equipment viability while ensuring compliance with rigorous safety standards.

Regulatory Foundations Shaping Preventive Crane Upkeep
Crane maintenance relies on Authoritative standards provide the essential backbone for machinery preservation efforts. First, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) outlines detailed protocols under 29 CFR 1910.179 specifically for overhead and gantry configurations. These mandate preventive maintenance schedules that align precisely with original equipment manufacturer (OEM) recommendations. Daily operations must include visual inspections for signs of wire rope fraying, hydraulic fluid leaks, or unusual structural deformations. Additionally, monthly documented assessments target critical hoisting mechanisms, braking systems, and limit switches to detect early performance deviations.
Next, comprehensive annual audits are required to scrutinize all load-bearing components for fatigue indicators, such as micro-crack initiation, corrosion pitting, or material thinning. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) B30.2 standard further reinforces this by specifying mandatory load testing at 125% of rated capacity following any major repair or component replacement. Failure to adhere to these guidelines not only invites operational interruptions but also exposes facilities to substantial legal liabilities under OSHA’s General Duty Clause. Therefore, only certified and trained personnel should conduct these evaluations to guarantee accuracy and safety.
Furthermore, environmental variables necessitate site-specific modifications. For example, in coastal or high-humidity installations, enhanced anti-corrosive coatings compliant with ISO 12944 classifications become essential to combat accelerated galvanic degradation. In contrast, arid or dusty environments prioritize sealed electrical enclosures and filtration systems to prevent particulate ingress that could compromise control circuits. Overall, this multi-layered regulatory structure transforms routine maintenance into a proactive system that consistently extends service intervals and operational reliability.

Structural Component Analysis for Prolonged Operational Integrity
Precise crane maintenance interventions can yield substantial durability improvements. Begin with wire rope management: electromagnetic non-destructive testing (eMAG) effectively identifies internal broken strands or corrosion at incipient stages. This early detection defers costly replacements and maintains safe load capacities. Meanwhile, lubrication protocols calibrated to actual duty cycles—following Fédération Européenne de la Manutention (FEM) guidelines—can reduce frictional wear by up to 40% in high-cycle applications, preserving rope diameter and tensile strength over extended periods.
Hoist and trolley assemblies require equivalent meticulous attention. Advanced finite element analysis, as employed by organizations like CETIM, simulates stress concentrations in girder welds under dynamic loading conditions. These models enable targeted reinforcements, such as gusset plates or weld overlays, before fatigue cracks propagate. Additionally, systematic torque verification of bolted connections—maintaining 80-90% of material yield strength—prevents vibrational loosening that often leads to trolley misalignment or runway rail damage.
Economically, these practices deliver compounding returns. A documented 2021 offshore drilling platform initiative implemented pressurized grease delivery systems for wire ropes, successfully postponing major overhauls and achieving a 15-20% reduction in operational expenditures over a five-year horizon. However, lapses in inspection protocols carry severe consequences. For instance, inadequate lubrication in concealed pivot points has historically resulted in catastrophic topping cylinder detachments even during lifts at merely 5% of rated capacity, underscoring the critical need for vigilance in hard-to-access areas.
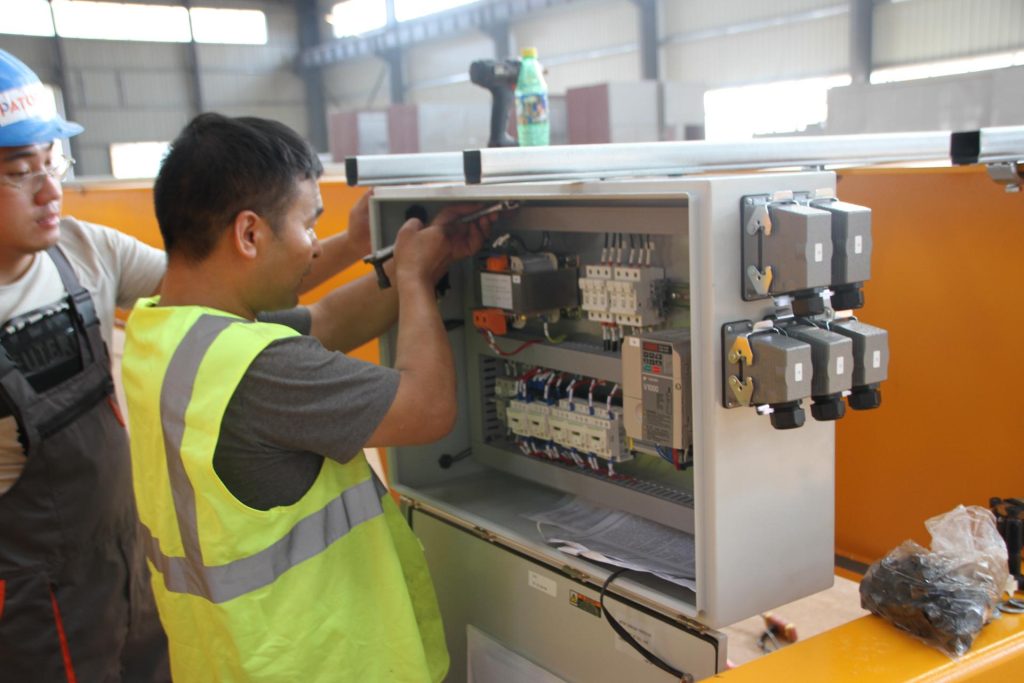
Fluid and Electrical System Dynamics in Crane Sustainability
Hydraulic and electrical subsystems function as the vital neural pathways of contemporary gantry and overhead cranes. Crane maintenance counters degradation that manifests through hydraulic fluid viscosity breakdown, contaminant accumulation, or electrical insulation deterioration. To mitigate these issues, scheduled fluid replacements must achieve ISO 4406 cleanliness codes of 18/16/13 or better. This purity level prevents pump cavitation, seal extrusion, and premature cylinder wear, thereby extending hydraulic actuator service life by 50% or more in demanding environments.
Electrical system integrity demands adherence to NFPA 70E arc-flash safety protocols, incorporating routine thermographic imaging to locate resistive hotspots in motor windings or contactors. Early identification averts insulation failures that could trigger widespread system blackouts. Besides, integrating Internet of Things (IoT) sensors for real-time monitoring of amperage fluctuations, voltage stability, and vibration signatures enables predictive maintenance algorithms. These tools shift interventions from fixed calendars to data-driven degradation curves, optimizing resource allocation.
A practical mining operation case illustrates the impact: implementing daily hydraulic leak detection protocols on a 150-ton crawler crane intercepted a minor seal breach before escalation. This prevented a projected multi-week shutdown, preserving annual production throughput valued at approximately $2.5 million. Thus, comprehensive subsystem governance not only doubles mechanical half-life but also establishes robust fault-tolerant architectures capable of withstanding unpredictable operational stresses.
Operator Proficiency and Load Management as Lifespan Catalysts
Crane maintenance is influenced by operator design and load-handling discipline directly influence long-term equipment endurance. ASME B30.5 explicitly requires operator certification programs that encompass dynamic load charting, sling angle calculations, and emergency response procedures. Abrupt accelerations exceeding 0.5g generate excessive inertial forces that accelerate boom deflection and rope sheave groove wear. In addition, refresher training via Crane Manufacturers Association of America (CMAA) Class C duty cycle simulations fosters precise swing damping techniques, significantly curtailing oscillatory stresses on end truck bearings and runway structures.
Effective load spectrum management further enhances resilience. Establishing operational ceilings at 80% of rated capacity per lift cycle minimizes cumulative fatigue damage, as quantified by Miner’s linear damage accumulation rule. A UK-based fabrication facility demonstrated this through virtual reality-based operator upskilling modules, which reduced documented overload incidents by 35% and correlated with a 25% extension in runway rail serviceability. Moreover, regular competency audits at a major logistics terminal extended gantry hoist functional viability by an additional 12 years. Skilled stewardship thus converts everyday operations into powerful longevity multipliers.
Environmental and Technological Mitigations for Enhanced Crane Viability
Ambient conditions—ranging from saline aerosols in marine settings to abrasive particulates in aggregate handling—necessitate tailored protective measures to maintain metallurgical integrity. Cathodic protection systems compliant with NACE SP0176 standards effectively inhibit galvanic corrosion in exposed lattice boom sections. Similarly, high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtered enclosures safeguard sensitive electronic controls from dust accumulation in quarry or cement plant deployments.
Technological advancements provide additional leverage. Artificial intelligence-driven vibration analysis platforms forecast tribological wear patterns with over 95% predictive fidelity, facilitating just-in-time component replacements that avoid unnecessary downtime. A construction consortium in Pune, India, applied this integrated approach to coastal gantry cranes by combining epoxy barrier coatings with embedded sensor arrays. The result was a 30% abatement in annual maintenance costs coupled with a full decade of added operational tenure, validating the synergy of environmental shielding and digital prognostics.
Empirical Illustrations of Maintenance-Driven Longevity Gains
Field deployments across sectors consistently substantiate these maintenance paradigms. At an Airbus final assembly line in Toulouse, CETIM engineers conducted residual life assessments using ultrasonic flaw detection combined with stochastic loading simulations. This rigorous evaluation certified legacy overhead manipulators for an additional 15-year service horizon, eliminating the need for $8 million in premature capital recapitalization. Likewise, a Pacific Northwest shipyard implemented monthly thermographic scanning protocols on mobile harbor cranes, successfully preempting a cascading hydraulic failure in a 200-ton unit during peak container handling seasons and maintaining uninterrupted project timelines.
These diverse real-world vignettes—from aerospace precision to heavy marine logistics—demonstrate that systematic non-destructive diagnostics fused with adaptive retrofit engineering reliably double asset amortization periods. The economic rationale for proactive, evidence-based stewardship becomes indisputable.
Strategic Implementation for Maximal Crane Endurance
To translate these insights into operational reality, adopt a phased implementation roadmap.
[1] initiates with baseline compliance audits aligned to OSHA periodicity requirements.
[2] establishes OEM-specific lubrication cadences, incorporating condition-monitoring triggers for adaptive intervals.
[3] deploys digital twin modeling for predictive anomaly detection and scenario forecasting. Quarterly cross-functional reviews—encompassing maintenance technicians, operators, and engineering leads—ensure ongoing alignment with evolving duty profiles and load spectra.
Finally, procure exclusively OEM-grade replacement components to eliminate compatibility variances and preserve warranty integrity.
In summary, achieving mastery in crane preservation requires harmonizing metallurgical foresight, thermodynamic system governance, human-centric operational discipline, and cutting-edge technological integration. By systematically embedding these protocols, industrial entities not only perpetuate peak equipment efficacy but also solidify foundational dependability, delivering measurable dividends in workplace safety, production throughput, and long-term fiscal prudence. OSHA 1910.179, ASME B30.2, ISO 4406, Konecranes Reliability Study, CETIM Residual Life Assessment.
Partner with CATET for Unmatched Crane Longevity and Performance
Elevate your operations with CATET Co., Ltd., a premier subsidiary of Dongqi Group and China’s trusted leader in crane and intelligent equipment manufacturing. Leveraging state-of-the-art R&D centers, automated production lines, and stringent international certifications—including ISO 9001, CE, and SGS—CATET engineers high-performance bridge cranes, gantry cranes, electric hoists, and customized material handling systems engineered for exceptional safety, precision, and extended service life via optimized crane maintenance design. Exported to over 90 countries, our solutions power critical sectors like steel mills, power plants, petrochemical facilities, logistics hubs, and automotive assembly lines, consistently delivering proven reliability that minimizes downtime and maximizes ROI.
Discover how CATET’s crane maintenance-optimized designs can double your equipment lifespan while ensuring seamless regulatory compliance. Contact our experts today to schedule a tailored consultation and unlock turnkey crane maintenance upgrades for your fleet.
How to Reach Us
WhatsApp/Skype/Hotline: +8615993097180
Email: [email protected]
Address: Room 808A, Building A, No. 4545, Songbai Road, Hewan Community, Matan Street, Guangming District, Shenzhen, China



