Electric Transfer Cart: Heavy Duty Pricing Guide & Custom Trackless Solutions | 2025
The electric transfer cart has revolutionized material handling across global industries. Specifically, these intelligent transport solutions move heavy loads from 1 to 1,500 tons efficiently. Moreover, they eliminate forklift congestion and reduce labor costs significantly. Understanding electric transfer cart specifications, pricing structures, and customization options helps facility managers optimize material flow. Consequently, this comprehensive guide explores heavy-duty systems, trackless transport innovations, and custom manufacturer capabilities backed by real-world data.
Understanding Electric Transfer Cart Technology
Basic Operating Principles
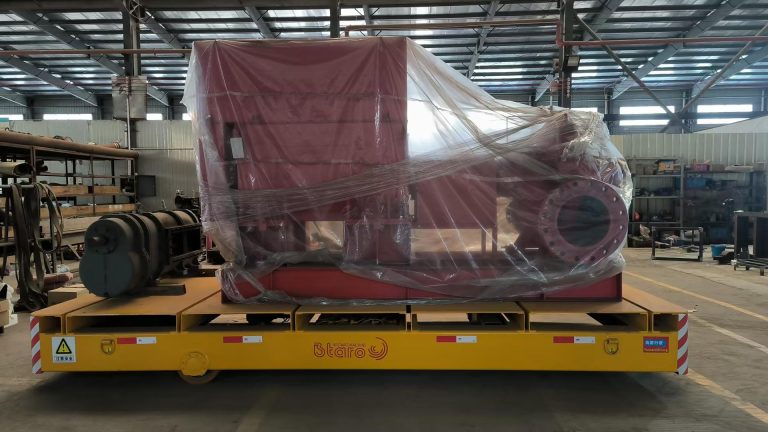
An electric transfer cart represents motorized material handling equipment designed for heavy industrial applications. The system consists of a robust steel platform. Additionally, it includes electric drive motors, power delivery system, and intelligent controls. Furthermore, these carts transport raw materials, finished products, dies, coils, and heavy machinery. Load capacities range from 500 kilograms to 1,500 metric tons. Meanwhile, travel speeds vary from 0.3 to 60 meters per minute depending on application requirements.
Structural Design and Materials
The platform typically uses Q235B or Q345B steel construction. Box beam or I-beam frames provide structural rigidity. Specifically, welded construction with reinforced cross-members supports distributed loading. Platform surfaces may feature flat decks. Alternatively, they include V-shaped cradles for coils, roller conveyors, or custom fixtures. Additionally, deck dimensions are fully customizable. Standard sizes range from 1,200mm x 1,800mm to 6,000mm x 12,000mm.
Drive System Components
Drive systems employ AC or DC electric motors with gearbox reducers. Motor power ranges from 1.5 kW for light loads. Conversely, heavy-duty applications require up to 45 kW. Therefore, wheel configurations include 4-wheel, 6-wheel, or 8-wheel designs. Heavy-duty systems use cast steel wheels (ZG55 material). These wheels feature 300-400 Brinell hardness. Meanwhile, polyurethane-coated wheels serve lighter applications. They provide floor protection effectively.
Rail-Mounted System Advantages
Electric transfer cart systems divide into two primary categories based on guidance methods. Rail-mounted systems follow steel tracks. Consequently, they provide precise positioning (±2-5mm accuracy). The tracks guide movement effectively. Moreover, they may provide electrical power. Rail-powered systems dominate heavy industrial applications. Specifically, they serve capacities exceeding 50 tons. The system uses conductive rails mounted alongside travel paths. Low-voltage DC power (36V or 48V) feeds through collector shoes. Consequently, this provides unlimited runtime for continuous operations.
Trackless Configuration Benefits
Trackless systems operate freely across floor surfaces. They offer maximum flexibility for multi-directional travel. Additionally, they eliminate track installation costs. These costs average $85-$150 per linear meter. Trackless electric transfer cart designs suit applications requiring flexible routing. They navigate freely between multiple destinations. Importantly, no fixed paths constrain movement. Battery power enables 4-12 hour operation. Runtime depends on capacity and usage intensity. Moreover, lithium-ion batteries provide 1,500-2,000 charge cycles. In contrast, lead-acid batteries offer 500-800 cycles. However, they cost less initially.
Heavy Duty Electric Transfer Cart Specifications and Pricing
Entry-Level Capacity Systems
Heavy duty electric transfer cart pricing varies substantially with load capacity and features. Entry-level systems rated for 1-5 tons cost $8,500 to $18,000. These represent basic configurations. Specifically, they typically feature 2,500mm x 1,500mm platforms. Additionally, battery power provides 6-8 hour runtime. Pendant control operation comes standard. Moreover, basic safety features are included. These systems serve light manufacturing effectively. Furthermore, they suit warehouse applications perfectly.
Mid-Range Industrial Solutions
Mid-range 10-20 ton capacity systems command $22,000 to $42,000. They offer larger platforms measuring 4,000mm x 2,500mm. Enhanced battery capacity delivers 8-12 hours runtime. Additionally, radio remote control options become available. Improved safety systems are standard. These units serve diverse industries effectively. Consequently, they represent the most popular capacity range. Market data shows 45% of installations fall within this category.
Heavy Industrial Configurations
Heavy industrial electric transfer cart systems rated for 30-50 tons range from $45,000 to $85,000. Platform dimensions expand significantly. Specifically, they reach 5,000mm x 3,500mm or larger. Power requirements increase substantially. Therefore, 18-35 kW motor capacity becomes necessary. These systems incorporate rail power supply. Consequently, they enable unlimited operation. Additionally, PLC-based control systems provide automation. Hydraulic steering mechanisms improve maneuverability. Furthermore, comprehensive safety interlocks protect operations.
Ultra-Heavy Duty Applications
Ultra-heavy duty configurations exceeding 100 tons cost $120,000 to $350,000. Custom engineering handles these extreme loads. Systems reach 500 tons capacity. However, premium pricing applies. Specialized structural design proves essential. Additionally, enhanced wheel assemblies distribute loads effectively. Moreover, sophisticated control systems ensure safety. These systems serve steel mills, shipyards, and aerospace facilities.
Manufacturer Price Comparisons
European manufacturers charge 35-50% premiums over Chinese suppliers. For example, a 20-ton system costs $32,000 from Chinese manufacturers. In contrast, European sources charge $48,000-$52,000. However, European systems offer distinct advantages. Specifically, precision engineering tolerances improve performance. Higher-grade component specifications extend service life. Additionally, extended warranty coverage (3-5 years versus 1-2 years) provides security. Furthermore, comprehensive technical support assists operations. Therefore, buyers must evaluate total cost of ownership carefully. Initial price alone proves insufficient for decisions.
Power Supply Systems Analysis
Battery-Powered System Economics
Battery-powered electric transfer carts offer maximum flexibility and simplicity. Lead-acid batteries cost $2,800-$4,500 for 10-ton systems. Lithium-ion upgrades add $6,500-$9,500 premium. However, lithium batteries provide significant advantages. Service life extends dramatically. Specifically, lead-acid lasts 3-5 years. In contrast, lithium batteries continue 8-12 years. Additionally, energy density increases 60-80%. This enables longer runtime. Alternatively, smaller battery packs suffice.
Charging Infrastructure Requirements
Charging time represents another critical difference. Lead-acid requires 8-10 hours for full charging. Meanwhile, lithium systems complete charging in 2-4 hours. This enables opportunity charging during breaks. Moreover, maintenance requirements virtually disappear with lithium. Lead-acid demands monthly water checks. Furthermore, terminal cleaning proves necessary. Conversely, lithium batteries operate maintenance-free. Therefore, long-term operational costs favor lithium significantly.
Cable Reel Power Systems
Cable reel powered systems suit applications up to 300 meters travel distance. The cable drum mechanism pays out cables automatically. Similarly, it retracts multi-conductor cables during return travel. Initial costs range from $4,200 to $7,800. Pricing depends on cable length and capacity. Standard configurations support 150-meter cables. Extended 300-meter systems cost $9,500-$14,000. Additionally, cable replacement occurs every 3-5 years. This costs $1,200-$2,800. Furthermore, the cable reel motor adds minor complexity. Periodic lubrication proves necessary.
Rail Power Infrastructure
Rail power supply provides unlimited operation for high-frequency applications. The conductive rail system costs $95-$165 per linear meter installed. A 100-meter system requires $9,500-$16,500 infrastructure investment. However, operational costs remain minimal. Electricity consumption averages $0.15-$0.45 per operating hour. Importantly, no batteries require replacement. Consequently, operations running over 8 hours daily achieve payback. Specifically, payback occurs within 18-30 months versus battery systems.
Real-World Power System Case Study
A steel manufacturing facility in Pennsylvania recently installed a 50-ton rail-powered electric transfer cart. The application involved coil handling operations. System specifications included several key features. First, a 6,000mm x 3,000mm platform with V-shaped cradle accommodated coil dimensions. Additionally, 200-meter rail system featured two parallel tracks. Moreover, 28 kW drive motors with variable frequency drives provided smooth control. Finally, PLC control enabled automated positioning. Positioning accuracy reached ±5mm consistently.
Equipment cost reached $72,000 for the complete cart. Rail installation added $32,000 (200m × $160/m). Electrical work contributed $11,500. Therefore, total project investment reached $115,500. This seemed substantial initially.
Power System ROI Analysis
The facility previously used an overhead crane for coil movement. Crane operation required certified operator at $32/hour. Additionally, a rigger earned $28/hour. Furthermore, crane availability created bottlenecks. These reduced throughput 15-20%. The electric transfer cart eliminated these constraints effectively. One operator controls multiple carts at $24/hour. Throughput increased 35% immediately. Meanwhile, labor costs decreased $142,000 annually. Furthermore, coil damage incidents decreased 65%. This saved $38,000 yearly. Consequently, payback occurred in just 15 months.
Trackless Electric Transfer Cart Custom Solutions
Differential Steering Systems
Custom trackless transport vehicles offer sophisticated steering mechanisms. These enable complex material flow patterns. Differential steering provides 360-degree rotation capability. Turning radius remains under 1.2 meters. Four-wheel independent drive motors enable advanced movements. Specifically, they allow in-place rotation. Additionally, diagonal travel becomes possible. Consequently, these systems navigate congested facilities efficiently. The differential steering system adds cost. Specifically, it increases price $6,500-$11,000. Final cost depends on capacity requirements.
Hydraulic Steering Technology
Hydraulic steering systems suit applications requiring smooth curved paths. They provide precise trajectory control effectively. Steering cylinders and control valves integrate with wheel assemblies. Operators control direction via steering wheel interface. This resembles automotive systems. Therefore, operation feels intuitive. This configuration handles loads exceeding 100 tons reliably. Moreover, hydraulic steering costs $8,500-$15,000. Pricing depends on system capacity. Maintenance requires annual hydraulic fluid changes. Additionally, seal inspection proves necessary.
Omni-Directional Mobility
Omni-directional Mecanum wheels represent advanced mobility solutions. Each wheel features passive rollers. These mount at 45-degree angles specifically. Independent servo motor control enables multiple movements. First, forward and backward travel works normally. Additionally, lateral sliding becomes possible. Furthermore, diagonal movement proves feasible. Finally, rotation occurs smoothly. Therefore, trackless electric transfer carts achieve unparalleled maneuverability. A 10-ton system with Mecanum wheels costs $52,000-$68,000. However, higher capacities face mechanical limitations. Practical limits reach approximately 25 tons currently.
AGV Navigation Technologies
Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) technology transforms basic electric transfer carts. Specifically, it creates intelligent autonomous systems. Laser navigation uses LIDAR sensors. These map facility environments accurately. The system calculates optimal paths dynamically. Moreover, it avoids obstacles automatically. Positioning accuracy reaches ±5-10mm consistently. Alternatively, magnetic strip navigation follows installed floor markers. Accuracy achieves ±10mm reliably. Furthermore, QR code navigation reads floor-mounted markers. This provides waypoint guidance effectively.
AGV Implementation Case Study
A food processing facility in California deployed AGV electric transfer carts recently. The goal involved automating raw material distribution. The system includes three 8-ton carts. Specifically, they feature laser SLAM navigation. Additionally, integrated WMS (Warehouse Management System) connectivity optimizes operations. Automatic charging stations enable continuous operation. Moreover, traffic management coordinates multiple vehicles. Each AGV cart cost $74,000. System integration added $28,000. Therefore, total investment reached $250,000 for the three-cart system.
AGV System Results
The facility previously employed six material handlers. They earned $17.50/hour operating manually-controlled carts. Additionally, forklifts served some operations. Annual labor costs exceeded $218,000. The AGV system reduced staffing dramatically. Specifically, two supervisors at $22/hour now manage operations. Annual labor costs dropped to $91,000. Material handling efficiency improved substantially. Specifically, it increased 45% through optimized routing. Continuous operation eliminated delays. Moreover, product tracking accuracy increased. It rose from 94% to 99.7%. Therefore, annual operational savings reached $127,000. Including efficiency gains worth $85,000 annually, total benefits exceeded $212,000. Consequently, payback period reached just 14.2 months.
Specialized Custom Engineering Features
Hydraulic Lifting Platforms
Custom trackless transport vehicle manufacturers provide extensive customization. These address unique material handling challenges effectively. Hydraulic lifting platforms enable height adjustment. Specifically, they move from floor level to 1,800mm elevation. This facilitates loading and unloading operations. Additionally, it enables equipment interface connection. Lifting capacity ranges from 5 to 150 tons. Hydraulic lift systems add $12,000-$38,000. Cost depends on capacity and travel height. Scissor lift mechanisms offer alternative solutions. They serve lower heights effectively. Moreover, they cost less than hydraulic cylinders.
Explosion-Proof Configurations
Explosion-proof configurations serve hazardous environments. These include chemical plants, paint booths, and grain handling facilities. All electrical components receive explosion-proof enclosures. They rate for specific hazard classifications. Motors, controls, and wiring meet ATEX standards. Alternatively, they comply with NEC 500/505 requirements. Additionally, spark-resistant wheels prevent ignition. Grounding systems eliminate static buildup. Explosion-proof certification increases costs substantially. Specifically, prices rise approximately 30-40%. For example, a standard 15-ton cart costs $32,000. The explosion-proof version reaches $44,000-$48,000.
Hazardous Environment Case Study
A chemical manufacturing plant in Texas required explosion-proof trackless electric transfer carts. The application involved solvent drum transport. Custom specification included several critical features. First, ATEX Zone 1 certification addressed flammable vapor environment. Additionally, 12-ton capacity handled operational requirements. The 4,000mm x 2,500mm platform accommodated drum configurations. Moreover, stainless steel construction provided corrosion resistance. Sealed lead-acid battery system eliminated spark hazards. Finally, intrinsically safe control circuits ensured safety. Total cart cost reached $67,000. This compared to $38,000 for non-explosion-proof equivalent. However, regulatory compliance mandated the investment. Importantly, no alternative handling method met safety requirements cost-effectively.
High-Temperature Operations
High-temperature operations demand specialized thermal protection. Steel mills, foundries, and forging operations expose equipment severely. Ambient temperatures reach 200-600°C. Heat-resistant materials prove essential. Additionally, active cooling systems protect critical components. Thermal shielding blocks radiant heat. Moreover, high-temperature wheels use specialized alloys. These withstand repeated heating cycles. However, these modifications add 25-35% to base equipment cost. Furthermore, component service life decreases. Therefore, increased maintenance frequency proves necessary.
Corrosion-Resistant Designs
Coastal environments present severe corrosion challenges. A port facility in Louisiana specified corrosion-resistant trackless electric transfer carts. The application involved container handling near saltwater. The harsh environment demanded extensive protection. First, hot-dip galvanized structural steel resisted corrosion. Additionally, stainless steel fasteners eliminated rust. Electrical boxes featured IP66 rating. Moreover, epoxy coating covered machined surfaces. Finally, sealed bearings used marine-grade grease. Standard 40-ton carts cost $62,000. Corrosion protection added $18,000. This represented a 29% increase. However, service life extended dramatically. Typical service reaches 12-15 years. In contrast, protected carts project 20+ years. Therefore, lifecycle cost analysis justified the investment clearly.
Rail-Mounted Electric Transfer Cart Systems
Conductive Rail Technical Specifications
Rail-powered electric transfer carts dominate heavy industrial applications. They provide unlimited operational duration. The system delivers 36V or 48V DC power. Power flows through conductive rails. These mount alongside travel paths. Alternatively, 380V or 660V AC systems serve high-power applications. Rectifier stations convert facility AC power. They produce required voltage accurately. Current capacity ranges from 100 to 800 amperes. This depends on motor power requirements. Additionally, it considers multiple cart operation.

Rail Installation Requirements
Installation requires precise rail alignment. Conductor spacing must maintain ±3mm tolerance. This applies over 10-meter spans. Rails mount on insulating supports. Support spacing ranges from 800-1,200mm. Protective covers shield conductors. They prevent debris accumulation. Additionally, they reduce contact hazards. Expansion joints accommodate thermal movement. Specifically, steel rails expand 0.012mm per meter per degree Celsius. Consequently, a 100-meter system experiences 36mm expansion. This occurs across 50°C temperature swings.
Multi-Cart Rail System Case
A steel rolling mill in Indiana installed an extensive rail system. The application required 300-meter dual-track configuration. This supported four 80-ton electric transfer carts. The installation included several components. First, 600 linear meters of conductive rail at $145/meter cost $87,000. Additionally, 48 rectifier stations provided 48V DC at 400A capacity. These cost $42,000. Protective covers and insulating supports added $28,000. Moreover, installation labor required 320 hours at $95/hour. This contributed $30,400. Therefore, total infrastructure cost reached $187,400.
However, the system serves multiple carts simultaneously. Additionally, it operates for decades. Amortized across four carts and 20-year service life, costs prove minimal. Infrastructure cost averages just $2,340 per cart annually. This represents excellent value.
Cable-Powered System Details
Cable reel powered electric transfer carts balance flexibility and unlimited duration. The system uses a rotating cable drum. It pays out multi-conductor cables as the cart travels. Spring-loaded rewind mechanisms retract cables automatically. They operate during return travel. Standard configurations support 150-meter travel distances. Extended systems reach 300 meters. However, they require enhanced cable drums. Additionally, stronger motors prove necessary.
Cable Specifications and Costs
Cable specifications include several configurations. Basic systems use 5-conductor cables. These provide power, control, and ground. Advanced systems need 8-12 conductors. They accommodate sensors and data transmission. Flexible construction withstands 10,000-15,000 winding cycles. Moreover, shielded designs prevent electromagnetic interference. Cable costs range from $12-$28 per meter. This depends on conductor count and specifications. Therefore, a 200-meter system requires $2,400-$5,600 in cables alone. Additionally, cable replacement occurs every 3-5 years.
Aerospace Cable Cart Application
An aerospace manufacturing facility in Washington implemented cable-powered systems. The application involved aircraft component handling. Specifically, wing sections weighing up to 35 tons required transport. Additionally, 180-meter travel distance separated work areas. The custom 40-ton cart featured several specifications. First, an 8,000mm x 3,500mm platform provided adequate space. Adjustable supports accommodated various wing configurations. Additionally, 22 kW drive motors delivered precision speed control. The 200-meter cable reel system enabled full travel. Finally, pendant control included emergency stop functions. Equipment cost reached $68,000. Installation added $8,500. Therefore, total investment reached $76,500.
Cable System Operating Costs
The cart operates 6-8 hours daily. It performs 15-20 movements routinely. Cable replacement occurs every 4 years. This costs $4,800. Annual maintenance averages $2,200. This includes cable drum lubrication. Additionally, guide roller replacement proves necessary. Moreover, electrical connection inspection occurs regularly. Electricity consumption averages 32 kWh daily. At $0.12/kWh, annual costs reach $1,400. Therefore, total annual operating cost reaches $5,500.
Conversely, the previous crane-based handling proved expensive. It required certified crane operators at $35/hour. Additionally, ground crew assisted operations. Labor costs exceeded $85,000 annually. Consequently, the electric transfer cart saves $79,500 yearly. This achieves payback in merely 11.6 months.
Selection Criteria and Specification Guidelines
Load Capacity Determination
Determining appropriate electric transfer cart capacity requires careful analysis. Maximum load weights need evaluation. Additionally, load distribution affects requirements. Rated capacity must exceed maximum anticipated load. Specifically, a 20-30% safety margin proves essential. For example, transporting 8-ton dies requires 10-12 ton rated cart. This margin accounts for dynamic loading. Acceleration and deceleration create additional forces. Furthermore, potential load overruns require consideration. Additionally, concentrated loads require structural reinforcement. This differs from distributed loading requirements.
Platform Dimension Planning
Platform dimensions must accommodate load geometry adequately. Clearance proves essential for safety. Standard practice adds 150-300mm clearance on all sides. Loading and unloading methods influence platform height. Ground-level loading favors low-profile carts. These measure 200-400mm height. Conversely, crane loading permits elevated platforms. Heights of 500-800mm provide better undercarriage access. Moreover, platform surface treatments vary. Options include non-slip coatings. Additionally, roller conveyors facilitate movement. Hydraulic clamps secure loads. Furthermore, custom fixtures maintain load security effectively.
Custom Platform Case Study
A metal fabrication shop in Michigan required specialized electric transfer carts. The application involved steel plate transport. Maximum plate dimensions reached 6,000mm x 3,000mm. Weight totaled 12 tons. The specification called for careful design. First, 15-ton capacity provided adequate safety margin. The platform measured 6,500mm x 3,500mm. This provided 250mm clearance around plates. Additionally, 350mm platform height enabled forklift loading. Removable side rails prevented plate shifting. Moreover, polyurethane-coated wheels protected the epoxy floor. The custom cart cost $41,000. Standard 15-ton carts with 5,000mm x 2,500mm platforms cost $32,000. Therefore, custom platform sizing added $9,000. This represented a 28% premium.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and ROI Calculations
Comprehensive Forklift Cost Comparison
Electric transfer cart economics compare favorably against alternatives. Forklift operation costs include multiple factors. Equipment purchase or lease requires $25,000-$65,000 per unit. Operator wages add $16-$24 per hour including benefits. Additionally, fuel or electricity costs $2,800-$6,500 annually per unit. Maintenance and repairs contribute $4,200-$7,800 annually. Moreover, insurance and safety compliance adds $2,200-$4,500 annually. Therefore, total 5-year cost of ownership for a single forklift reaches $175,000-$285,000.
Overhead Crane Alternative Analysis
Overhead crane systems require significant infrastructure investment initially. A 20-ton bridge crane installation costs $95,000-$165,000. Operating expenses prove substantial. Certified crane operators earn $28-$38 per hour. Annual inspections and maintenance cost $4,500-$8,500. Additionally, periodic component replacement proves necessary. Hoists, wheels, and cables require eventual replacement. Furthermore, cranes offer limited flexibility. They cannot transport materials beyond runway coverage. This requires additional handling equipment.
Electric Transfer Cart Economics
Electric transfer carts cost $22,000-$42,000 for 10-20 ton capacities. Installation adds moderate expense. Operating costs remain reasonable. Operators earn $18-$24 per hour. Lower certification requirements reduce wages. Additionally, electricity averages $1,200-$2,800 annually. Maintenance costs reach $1,800-$3,500 annually. Moreover, insurance needs remain minimal. General liability suffices. Therefore, 5-year ownership costs reach $65,000-$105,000. This represents 40-60% less than forklifts or cranes.
Productivity Enhancement Metrics
Beyond direct cost savings, electric transfer carts enhance operational efficiency. Material handling time typically decreases 40-65% versus forklifts. For instance, a manufacturing facility moved 15-ton loads 60 meters regularly. Forklifts required 12 minutes per cycle. Electric transfer carts reduced cycle time to 4.5 minutes. This achieved a 62% improvement. Consequently, throughput increased from 5 to 13 movements per hour.
Floor Space Optimization
Floor space utilization improves significantly with carts. Forklifts require wide aisles for turning. Specifically, they need 3.5-4.5 meters clearance. Electric transfer carts travel on defined paths. They require only 2.5-3.0 meter clearances. Additionally, they may utilize overhead space. They operate below crane systems simultaneously. For example, a 50,000 square foot facility reclaimed 3,200 square feet. This represents 6.4% space recovery. At $15/sq ft annual carrying cost, this provides $48,000 yearly value.
Safety Performance Improvements
Safety improvements deliver tangible financial benefits. Forklift accidents cost U.S. businesses substantially. Specifically, they exceed $135 million annually per OSHA data. Electric transfer carts virtually eliminate common forklift hazards. These include tipping, falling loads, pedestrian strikes, and rack collisions. A Midwestern manufacturer reduced recordable accidents dramatically. Incidents decreased from 4 to 0.3 per year post-implementation. Consequently, workers compensation premiums decreased $32,000 annually. This reflected improved safety performance directly.
Comprehensive ROI Case Study
A food processing facility in Wisconsin provides excellent ROI demonstration. The company installed three 12-ton battery-powered trackless electric transfer carts. These replaced two forklifts and manual pallet jacks. The detailed investment included several components. Three carts at $34,000 each totaled $102,000. Charging infrastructure and electrical work added $8,500. Additionally, operator training and system commissioning cost $3,200. First-year maintenance contract contributed $4,500. Therefore, total investment reached $118,200.
Pre-Implementation Cost Structure
Pre-implementation costs included substantial expenses. Two forklifts operated at $3,200 monthly lease. Annual costs reached $76,800. Four material handlers earned $18/hour including benefits. Their wages totaled $149,760 annually. Propane fuel averaged $640 monthly. Annual fuel costs reached $7,680. Additionally, forklift maintenance and repairs cost $8,400 annually. Product damage averaged $18,000 annually. Therefore, total annual costs exceeded $260,640.
Post-Implementation Results
Post-implementation costs decreased substantially. Two cart operators at $20/hour handle all material movement effectively. Including benefits, annual costs reach $83,200. Electricity for cart charging averages $285 monthly. Annual electricity costs total $3,420. Annual maintenance contracts cover all service. These cost $6,500 annually. Product damage decreased 75%. Costs dropped to $4,500 annually. Therefore, total annual costs reached $97,620. This represents savings of $163,020 annually. Simple payback period calculated to just 8.7 months.
Extended Benefits Analysis
Beyond direct savings, productivity improvements generated additional value. Material handling capacity increased 35%. This enabled production volume growth. Specifically, the facility processed 4,200 additional tons annually. This contributed $86,000 additional profit. Therefore, total first-year benefit reached $249,020. The investment achieved 211% first-year ROI. Over 10-year equipment life, benefits accumulate substantially. Net present value exceeded $1.8 million. This calculation used 6% discount rate.
Ready to Optimize Your Material Handling with Electric Transfer Carts?
Contact us today for expert consultation on heavy-duty systems. Additionally, we provide custom trackless solutions. Our engineering team analyzes your specific requirements carefully. We consider load capacities, travel distances, and environmental conditions. Moreover, budget parameters receive full attention. Furthermore, we provide detailed quotations with transparent pricing within 24 hours.
Our Comprehensive Services Include:
- Custom design engineering with 3D modeling and FEA analysis
- Multiple power supply options (battery, rail, cable reel)
- AGV integration and automation systems
- Professional installation and commissioning
- Operator training programs (8-12 hours)
- 24-month parts and labor warranty
- Preventive maintenance contracts
- 24/7 technical support hotline
Safety Disclaimer: This article provides general information about electric transfer carts for educational purposes. Actual installations must be performed by qualified professionals. All applicable codes, standards, and manufacturer specifications must be followed. Consult licensed engineers and certified installation contractors for your specific project requirements. OSHA 1910.178 and relevant material handling standards apply.
Technical Specifications Disclaimer: All technical data, specifications, and pricing referenced represent general industry standards. These are approximate values. Specific projects may require different parameters. Unique conditions, local regulations, or engineering requirements may apply. Always obtain formal quotations and engineering approval. This must occur before proceeding with equipment purchase and installation.
External Resources:



