What is an Electric Hoist Winch? Complete Technical Guide to Motorized Lifting and Pulling Equipment for Industrial Applications
Introduction: Understanding Electric Hoist Winch Technology

An electric hoist winch represents a motorized lifting device that utilizes electric power to raise, lower, position, and transport heavy loads through vertical or near-vertical movement. These sophisticated mechanical systems convert electrical energy into mechanical motion via electric motors, driving drums or chain wheels that wind cables, ropes, or chains to perform lifting operations. Unlike manual hoists requiring physical effort or winches designed primarily for horizontal pulling, electric hoist winches specifically excel at vertical lifting applications requiring power, precision, and sustained operation.
The fundamental distinction between electric hoists and electric winches centers on operational orientation and load handling characteristics. Electric hoists lift loads vertically and suspend them mid-air with load-holding brakes preventing unintended descent. Conversely, electric winches pull objects horizontally across surfaces, lacking specialized braking systems necessary for safe vertical suspension. This critical difference determines appropriate equipment selection for specific applications, with misapplication potentially causing dangerous operational failures.
Global market data demonstrates the essential role electric hoist winches play across industrial sectors. The electric hoist market reached 2.1-2.4 billion USD in 2024 and projects growth to 4.2 billion USD by 2034 at 5.6-5.7% CAGR. Furthermore, the broader electric winch market valued at 117-133 billion USD in 2024 anticipates expansion to 330 billion USD by 2037 at 8.3% CAGR. Load capacities range from 500 kilograms for light-duty applications to over 100 tons for heavy industrial configurations, serving construction, manufacturing, mining, marine, and entertainment industries requiring reliable powered lifting solutions.
Fundamental Components and Operating Principles
Electric Motor and Power System
The electric motor serves as the heart of any electric hoist winch system, converting electrical energy into rotational mechanical energy. Three-phase AC motors dominate industrial applications, delivering robust performance with capacities from 1.5 kW for light-duty units to 75 kW for heavy industrial configurations. Single-phase motors suit smaller portable units where three-phase power remains unavailable. Moreover, motor selection considers voltage requirements, with common specifications including 110V, 220V, 380V, and 440V matching regional electrical standards.
Variable frequency drives increasingly control modern electric hoist winch motors, enabling precise speed regulation, soft starting, and smooth acceleration reducing mechanical stress. These advanced control systems improve positioning accuracy while extending component service life through reduced shock loading. Furthermore, thermal overload protection prevents motor damage from excessive current draw, automatically shutting down operations before permanent damage occurs.
Drum and Cable System Architecture
Wire rope hoists utilize cylindrical drums storing steel wire rope during lifting operations. Drum diameter directly influences rope service life, with larger diameters reducing bending stress and extending rope longevity. Industry standards typically specify minimum drum diameters of 16-20 times rope diameter, ensuring acceptable bending radius. Additionally, rope grooving on drum surfaces guides cable winding, preventing crossover and ensuring uniform layer formation throughout multiple wraps.
Rope selection balances strength, flexibility, and wear resistance. Construction types include 6×19, 6×37, and 8×19 configurations, with numbers indicating strand count and wires per strand. For example, 6×37 rope contains six strands with 37 wires each, providing excellent flexibility suitable for frequent bending over sheaves and drums. Galvanized or stainless steel ropes resist corrosion in harsh environments including marine applications and chemical processing facilities.
Chain Hoist Mechanisms
Electric chain hoists employ load chains rather than wire rope, utilizing sprocket wheels engaging chain links for lifting operations. The chain drive offers several advantages including compact design, minimal maintenance requirements, and excellent positioning precision. Specifically, chain engagement with sprockets creates positive drive eliminating slippage concerns present in friction-based systems.
Load chains conform to international standards including Grade 80 or Grade 100 specifications, indicating minimum tensile strength. Chain construction features welded links heat-treated for enhanced strength and wear resistance. Moreover, special low-headroom designs minimize hook-to-trolley distance, maximizing usable lift height in facilities with limited vertical clearance.
Braking Systems and Load Holding
Reliable braking systems represent critical safety features preventing uncontrolled load descent. Mechanical brakes automatically engage when motor power ceases, using spring pressure forcing friction pads against brake discs. This fail-safe design ensures load holding even during power failures or emergency stops. Additionally, electromagnetic brakes offer precise holding force and rapid engagement improving operational responsiveness.
Regenerative braking systems in advanced electric hoist winches capture energy during lowering operations, feeding power back into electrical systems. This technology reduces energy consumption by 15-30% in high-duty-cycle applications while decreasing brake wear through reduced reliance on friction braking. Consequently, organizations operating intensive lifting operations achieve measurable operational cost reductions while supporting sustainability initiatives.
Control Systems and Safety Features
Pendant control stations provide operator interface through push-button controls managing up/down movement and optional traverse functions. Ergonomic pendant design reduces operator fatigue during extended operations while maintaining intuitive operation. Radio remote controls enhance safety by enabling operators to maintain optimal viewing positions throughout lifting operations, eliminating blind spots common with fixed pendant controls.
Limit switches prevent over-travel in both up and down directions, protecting equipment from damage caused by excessive rope spooling or load contact with structural components. Emergency stop functions enable immediate operational cessation during dangerous conditions. Furthermore, overload protection systems refuse lift commands exceeding rated capacity, eliminating dangerous overload situations that could cause equipment failure or catastrophic accidents.
Types and Configurations of Electric Hoist Winches
Electric Wire Rope Hoists
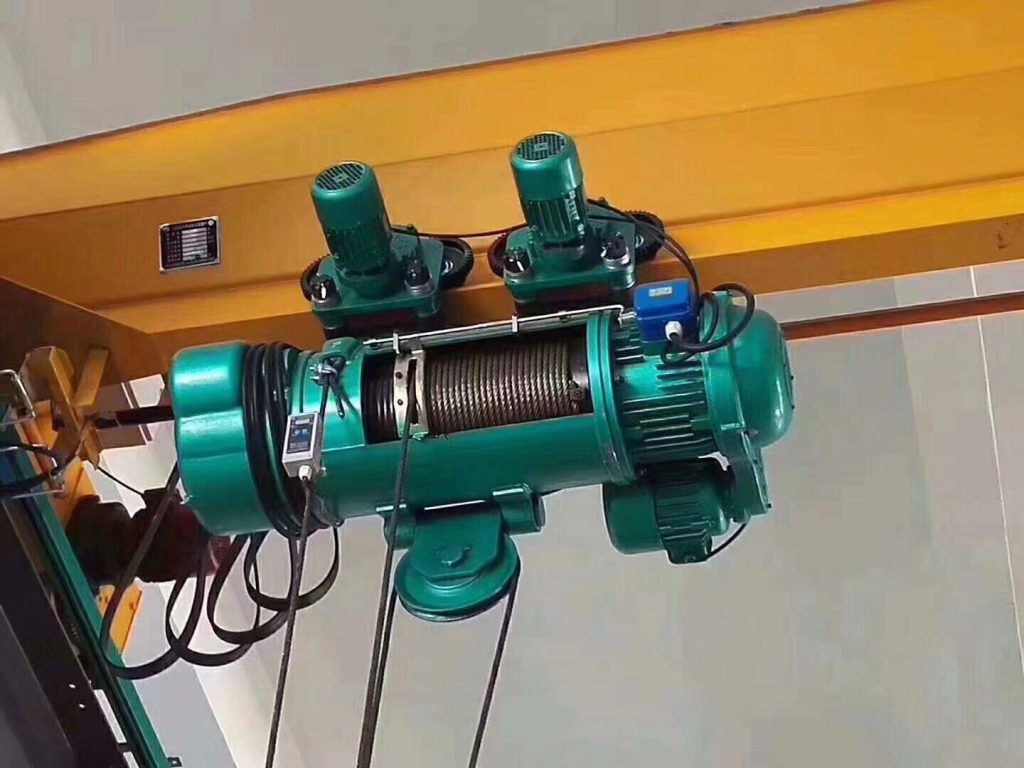
Electric wire rope hoists dominate heavy-duty industrial applications, offering load capacities from 1 ton to over 100 tons. These robust devices feature steel wire rope wound on grooved drums, providing long lifting heights exceeding 100 meters for deep-lift applications including mining shafts and high-rise construction. The wire rope construction delivers excellent strength-to-weight ratio enabling substantial load handling in relatively compact packages.
Key Features:
- High load capacity – Handles 1-100+ tons depending on configuration
- Extended lifting heights – Accommodates lifts exceeding 100 meters
- Fast operational speeds – Lifting rates reach 20 meters per minute
- Durable construction – Suitable for demanding industrial environments
- Multiple reeving options – Single, double, or quadruple rope configurations multiply capacity
Wire rope hoists suit applications including steel mills, shipyards, heavy manufacturing, and construction sites requiring maximum lifting capability. However, rope inspection and replacement represent significant maintenance considerations, with rope service life depending on duty cycle, load characteristics, and environmental conditions.
Electric Chain Hoists
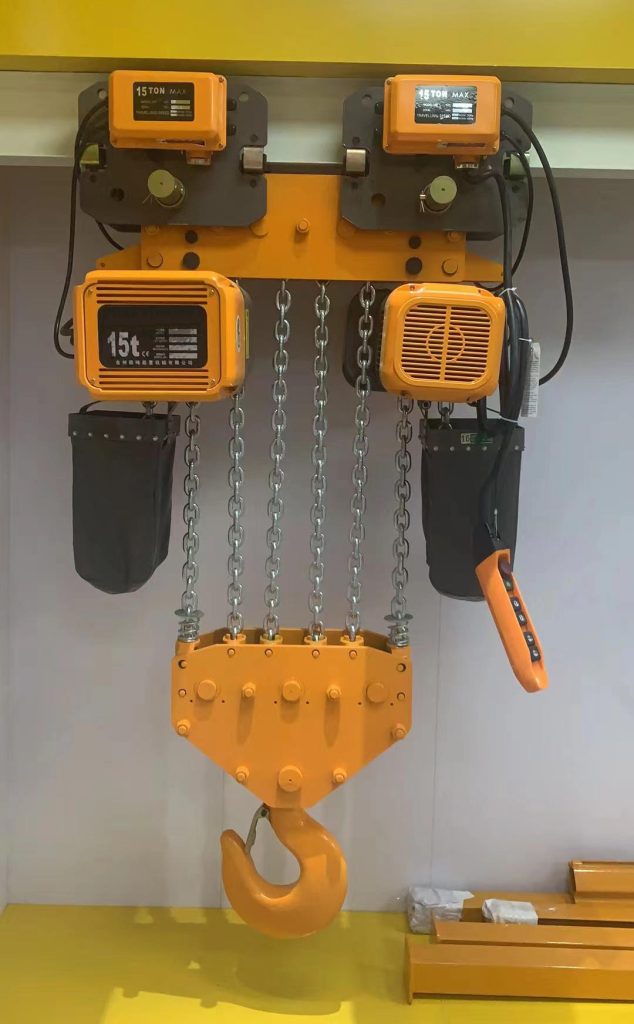

Electric chain hoists provide versatile lifting solutions for loads ranging from 250 kilograms to 10 tons, with compact designs ideal for space-constrained installations. The load chain engages sprocket wheels creating positive drive without slippage concerns. Moreover, the modular design simplifies maintenance with easily replaceable chain sections and standardized components.
Key Advantages:
- Compact design – Minimal headroom requirements maximize usable lift
- Low maintenance – Chain durability reduces service frequency
- Precise positioning – Positive drive prevents load drift
- Quiet operation – Suitable for noise-sensitive environments
- Easy installation – Lightweight construction simplifies mounting
Chain hoists excel in assembly operations, maintenance facilities, warehouses, and workshops where moderate loads require frequent positioning adjustments. The compact envelope suits retrofitting into existing facilities with height constraints. Additionally, the standardized chain and sprocket design enables cost-effective spare parts availability.
Portable vs. Stationary Configurations
Portable electric hoist winches incorporate integral mounting hardware enabling quick installation and relocation between work sites. Compact designs with integrated lifting points facilitate crane-assisted positioning or manual handling depending on unit weight. These versatile devices suit construction projects, maintenance operations, and temporary installations requiring flexible lifting capability without permanent infrastructure.
Stationary electric hoist winches mount permanently to building structures, monorails, or bridge cranes forming integrated material handling systems. The fixed installation enables higher capacity ratings, extended duty cycles, and optimized positioning for specific applications. Furthermore, hardwired electrical connections eliminate flexible cable management concerns present in portable applications.
Single-Speed vs. Dual-Speed Operation
Single-speed electric hoist winches operate at constant lifting velocity, providing straightforward control and economical pricing suitable for applications without demanding positioning requirements. The consistent speed simplifies operator training while reducing control system complexity and cost.
Dual-speed configurations offer high-speed gross positioning and low-speed precision control within single units. Typically, high speed operates at 8-10 meters per minute while low speed reduces to 1-2 meters per minute enabling accurate load placement. This versatility proves valuable in assembly operations, precision manufacturing, and applications requiring both rapid transport and exact positioning.
Explosion-Proof Designs for Hazardous Environments
Specialized explosion-proof electric hoist winches serve hazardous locations featuring flammable gases, combustible dusts, or volatile atmospheres where standard equipment could create ignition sources. These certified devices incorporate sealed motor housings, special electrical enclosures, and non-sparking materials preventing dangerous atmospheric ignition.
Compliance with ATEX, IECEx, or Class I Division 1 certifications demonstrates suitability for specific hazardous classifications. Applications include chemical processing, oil and gas facilities, paint spray operations, and grain handling where explosion risks mandate specialized equipment. However, explosion-proof construction commands premium pricing justified by critical safety requirements and regulatory compliance.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases
Construction and Infrastructure Projects
Construction sites extensively deploy electric hoist winches for material lifting, equipment positioning, and structural assembly. Tower cranes incorporate massive wire rope hoists handling building materials to extreme heights during skyscraper construction. Smaller portable hoists facilitate equipment installation, HVAC mounting, and steel erection throughout project lifecycles.
Bridge construction utilizes specialized hoists for girder placement, deck panel installation, and cable tensioning. The precise control and substantial capacity enable safe handling of multi-ton structural components while maintaining construction schedules. Moreover, electric operation eliminates hydraulic fluid contamination concerns important for environmental protection during waterway construction projects.
Manufacturing and Assembly Operations
Manufacturing facilities integrate electric hoist winches throughout production processes for raw material handling, work-in-process movement, and finished goods transport. Assembly lines incorporate chain hoists positioning components during assembly sequences, with dual-speed control enabling rapid gross positioning and precise final placement.
Metal fabrication shops deploy hoists for plate handling, welded assembly manipulation, and machining operation load/unload cycles. The consistent lifting capacity and reliable positioning improve production efficiency while reducing workplace injury risks from manual material handling. Furthermore, integration with manufacturing execution systems enables automated material flow coordinating with production schedules.
Case Study: An automotive component manufacturer implemented twenty 2-ton electric chain hoists throughout their assembly facility. The synchronized hoists handle engine blocks, transmission assemblies, and chassis components with positioning accuracy within ±5mm. The installation delivered 25% productivity improvement in assembly operations while eliminating worker compensation claims related to manual material handling, achieving complete ROI within 18 months.
Mining and Resource Extraction
Mining operations utilize heavy-duty electric hoist winches for shaft sinking, equipment deployment, material extraction, and personnel transport. Specialized mine hoists handle extreme loads exceeding 50 tons while operating in harsh environments featuring dust, moisture, and temperature extremes. The robust construction and oversized safety factors ensure reliable operation in applications where failures pose catastrophic safety and economic consequences.
Ore extraction hoists operate continuously raising excavated material from underground workings to surface processing facilities. These high-duty-cycle applications demand premium components, sophisticated monitoring systems, and rigorous maintenance programs maintaining operational reliability essential for mine productivity targets.
Marine and Offshore Applications
Marine environments present unique challenges including corrosion from saltwater exposure, dynamic loading from vessel motion, and explosive atmosphere classifications. Specialized marine-grade electric hoist winches incorporate stainless steel or heavily coated components resisting corrosion while meeting classification society requirements from organizations including ABS, DNV, and Lloyd’s Register.
Offshore oil platforms deploy explosion-proof hoists for equipment handling, supply operations, and maintenance activities in hazardous Zone 1 and Zone 2 classified areas. The certified equipment prevents ignition of hydrocarbon atmospheres while delivering reliable performance in harsh offshore conditions featuring wind, waves, and corrosive spray.
Entertainment and Stage Rigging
Theaters, concert venues, and television studios extensively utilize electric chain hoists for stage rigging, lighting suspension, and scenery movement. These specialized entertainment hoists feature silent operation preventing acoustic interference during performances, variable speed control enabling smooth scenic transitions, and redundant safety systems protecting performers and audiences.
Modern stage rigging systems incorporate dozens of synchronized hoists controlled through sophisticated automation systems creating complex three-dimensional movements enhancing production value. Entertainment hoists undergo regular inspection and certification verifying safe operation for suspended loads above performers and audiences, with regulatory requirements exceeding general industrial standards.
Selection Criteria for Electric Hoist Winches
Load Capacity and Safety Factor Determination
Proper capacity selection requires comprehensive analysis of maximum load weight including materials, lifting hardware, and rigging equipment. Industry standards recommend minimum safety factors of 5:1 for general industrial applications, meaning rated capacity should exceed maximum working load by at least five times. Critical applications including personnel lifting mandate 10:1 safety factors ensuring adequate margins under worst-case scenarios.
Dynamic loading from acceleration, deceleration, and shock must be considered beyond static weight calculations. Impact factors typically add 25-50% to static loads accounting for operational dynamics. Furthermore, applications experiencing frequent shock loading or outdoor exposure to wind forces require additional capacity margins maintaining adequate safety under all operational conditions.
Lift Height and Speed Requirements
Lifting height determines rope or chain length and influences overall system design. Standard lift heights range from 3 meters for workshop applications to over 100 meters for high-rise construction or mine shaft installations. Longer lifts require larger drum diameters and may necessitate multi-layer rope winding or extended chain storage capacity.
Operational speed directly impacts productivity with typical ranges spanning 1-20 meters per minute depending on application requirements. High-speed hoists improve cycle times in material handling operations but command premium pricing and require additional safety considerations. Conversely, precision applications prioritize slow-speed control over maximum velocity, with dual-speed configurations providing optimal versatility.
Duty Cycle Classification and Service Life
Duty cycle rating indicates operational intensity and determines component specifications, with classifications ranging from M1 (occasional use) to M8 (continuous heavy-duty operation). Light-duty M1-M3 classifications suit maintenance facilities and workshops with intermittent lifting requirements. Medium-duty M4-M5 ratings accommodate manufacturing and warehouse applications with regular operational patterns.
Heavy-duty M6-M8 classifications serve intensive continuous operations including steel mills, foundries, and high-volume material handling where hoists operate most of each shift. The enhanced components, oversized safety factors, and premium materials justify higher initial investment through extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements. Mismatching duty classification to actual usage patterns causes premature failure and safety risks.
Power Supply and Electrical Requirements
Available electrical infrastructure determines motor specifications with three-phase power preferred for units exceeding 2 kW due to superior efficiency and starting characteristics. Voltage requirements must match facility electrical systems with common specifications including 220V single-phase, 380V/440V three-phase, and occasionally 480V or 575V for larger units.
Portable applications may require single-phase motors accommodating standard electrical outlets despite reduced efficiency and capacity limitations. Additionally, voltage drop calculations ensure adequate conductor sizing for installation distances, preventing motor damage from insufficient voltage especially during starting transients requiring 3-5 times running current.
Environmental Conditions and Protection
Operating environment significantly influences equipment specification and longevity. Temperature extremes affect motor performance, lubrication characteristics, and material properties. High-temperature applications (exceeding 40°C) require special insulation classes and oversized motors compensating for reduced cooling efficiency. Low-temperature environments (below -20°C) necessitate special cold-weather lubricants and heater-equipped motor housings.
Corrosive atmospheres including chemical processing, marine environments, and outdoor installations require stainless steel components or protective coatings resisting degradation. IP (Ingress Protection) ratings indicate environmental sealing with IP54 providing adequate protection for indoor industrial use while IP65 or IP66 suit outdoor or washdown applications. Explosive atmospheres mandate certified explosion-proof construction complying with ATEX, IECEx, or NEC hazardous location classifications.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper Mounting and Structural Support
Correct installation fundamentally impacts electric hoist winch safety, performance, and longevity. Support structures must provide adequate strength accommodating dynamic loads including impact forces from sudden stops or shock loading. Structural engineers should verify building capacity or design supplemental support systems where existing structures prove inadequate for intended loads.
Mounting orientation must align with manufacturer specifications with many hoists requiring specific angles preventing lubricant migration or mechanical binding. Trolley-mounted installations demand precise rail alignment maintaining straightness and levelness within specified tolerances. Misalignment causes excessive wheel wear, increased power consumption, and potential derailment creating dangerous situations.
Inspection and Testing Protocols
Systematic inspection programs identify developing issues before catastrophic failures occur. Daily pre-operation checks include visual inspection of wire rope or chain condition, verification of proper brake operation, and testing of limit switches and emergency stops. Operators should listen for unusual noises indicating mechanical problems requiring investigation.
Monthly detailed inspections examine rope or chain for wear, corrosion, and damage requiring replacement. Load test procedures verify adequate capacity and proper brake function under operational loading. Annual comprehensive inspections may include disassembly for internal component examination, non-destructive testing of critical elements, and certification by qualified inspectors documenting compliance with safety standards.
Lubrication and Component Service
Regular lubrication maintains efficient operation and extends component service life. Gear reducers require periodic oil changes every 2,000-5,000 hours depending on duty cycle and operating conditions. Wire rope needs regular lubrication maintaining flexibility and resisting corrosion, with application frequency depending on environmental exposure and operational intensity.
Load chain requires minimal lubrication but benefits from periodic cleaning removing accumulated dirt and debris. Bearing assemblies in trolley wheels, drums, and motor supports need greasing at intervals specified by manufacturers, typically every 500-1,000 operating hours. Proper lubricant selection considering temperature range and operational conditions proves essential for adequate protection.
Wire Rope and Chain Replacement Criteria
Wire rope requires replacement when visible deterioration exceeds acceptable standards including broken wires, corrosion, mechanical damage, or diameter reduction. Specific retirement criteria typically specify replacement when six randomly distributed broken wires appear in one rope lay, three broken wires in one strand, or diameter decreases exceed 7% of nominal size.
Load chain replacement becomes necessary when wear, elongation, or damage compromise integrity. Measurable criteria include pitch elongation exceeding 3% of original dimension, link wear reducing thickness by 10%, or any cracked or deformed links. Organizations maintaining critical lifting operations should implement proactive replacement schedules replacing rope or chain before reaching retirement criteria, eliminating unexpected failures during operations.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Initial Investment Considerations
Electric hoist winch costs vary dramatically based on capacity, configuration, and features. Basic 1-ton electric chain hoists start around $800-$2,000 for commercial-grade units. Industrial 5-ton wire rope hoists range from $3,000-$8,000 depending on lift height and features. Heavy-duty 20-ton configurations require investments of $15,000-$40,000 per unit.
Explosion-proof certifications add 30-50% premiums to equivalent standard models. Dual-speed operation increases costs 15-25% over single-speed alternatives. Installation expenses including structural modifications, electrical work, and commissioning typically add 20-40% to equipment costs. Organizations should budget comprehensively for complete system implementation avoiding unexpected cost overruns.
Operational Cost Advantages
Energy consumption for electric hoist winches remains modest in intermittent-duty applications with typical units drawing 2-15 kW during lifting operations. Annual energy costs range from $200-$2,000 depending on capacity, duty cycle, and local electrical rates. However, continuous heavy-duty operations accumulate significant energy expenses warranting consideration of high-efficiency motors and regenerative braking systems reducing consumption.
Compared to manual hoists, electric hoist winches dramatically improve productivity enabling faster cycle times and reduced labor requirements. Additionally, the elimination of physical lifting effort reduces workplace injuries and associated costs including workers compensation premiums, lost time, and reduced productivity. These operational benefits typically justify equipment investments through rapid ROI calculations.
Total Cost of Ownership
Long-term ownership costs encompass equipment purchase, installation, energy consumption, maintenance, and eventual replacement. Preventive maintenance programs including inspections, lubrication, and wear component replacement typically cost $500-$3,000 annually depending on unit size and duty cycle. Well-maintained electric hoist winches deliver 15-25 year service lives providing excellent long-term value.
Case Study: A distribution center invested $45,000 implementing ten 2-ton electric chain hoists replacing manual lifting practices. Annual operational savings totaling $28,000 resulted from improved productivity (40% faster cycle times), reduced labor requirements (elimination of two-person lifts), and decreased injury-related costs (zero manual handling injuries in first 24 months). The installation achieved complete ROI within 20 months with ongoing operational benefits throughout anticipated 20-year equipment lifespan.
Safety Standards and Regulatory Compliance
OSHA and ASME Requirements
United States operations must comply with OSHA regulations governing overhead and gantry cranes (29 CFR 1910.179) and ASME B30.16 standards for overhead hoists. These requirements mandate regular inspections, operator training, load testing, and maintenance documentation. Furthermore, equipment must feature specific safety devices including overload protection, limit switches, and audible warning signals.
Violations of OSHA crane and hoist regulations result in substantial penalties while creating liability exposure for workplace accidents. Organizations should implement comprehensive compliance programs ensuring regulatory adherence while protecting worker safety. Documented inspection records, operator training certifications, and maintenance logs demonstrate compliance during regulatory audits or accident investigations.
European CE Marking and Machinery Directive
European markets require CE marking demonstrating compliance with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and relevant harmonized standards including EN 14492 for wire rope hoists and EN 14492-2 for chain hoists. Manufacturers must conduct conformity assessments, prepare technical documentation, and affix CE marking before equipment sale or installation within EU member states.
Additionally, ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU governs equipment intended for explosive atmospheres, with specialized certification requirements for Ex-rated hoists. Import of non-compliant equipment risks customs seizure, substantial fines, and criminal liability for serious non-compliance. Purchasers should verify proper CE marking and obtain Declaration of Conformity documentation ensuring regulatory compliance.
Operator Training and Certification
Qualified operators prove essential for safe electric hoist winch operation. Training programs should address equipment capabilities and limitations, proper rigging techniques, load calculation methods, inspection procedures, and emergency response protocols. Many jurisdictions mandate formal operator certification demonstrating competency through written and practical examinations.
Refresher training maintains operator skills with recommended intervals of 2-3 years or following significant equipment changes, accidents, or near-miss incidents. Documentation of operator training provides evidence of due diligence during accident investigations or regulatory compliance audits. Organizations should implement systematic training programs ensuring all operators receive proper instruction before independent operation authorization.
Conclusion: Electric Hoist Winches as Essential Industrial Equipment
Electric hoist winches represent fundamental material handling equipment enabling safe, efficient lifting operations across diverse industrial applications. The technology’s evolution from simple motor-driven drums to sophisticated computer-controlled systems reflects ongoing advancement addressing increasing performance demands, safety requirements, and productivity expectations. Load capacities spanning 500 kilograms to over 100 tons accommodate applications from workshop maintenance to heavy industrial material handling.
Market growth projections indicating the electric hoist market reaching 4.2 billion USD by 2034 and electric winch markets expanding to 330 billion USD by 2037 demonstrate sustained demand driven by construction activity, manufacturing automation, and infrastructure development worldwide. Moreover, technological innovations including variable frequency drives, regenerative braking, and smart monitoring systems enhance capability while reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Organizations evaluating material handling solutions should carefully assess electric hoist winch advantages including consistent lifting capacity, operational efficiency, safety features, and long-term reliability. Proper equipment selection considering load requirements, duty cycles, environmental conditions, and regulatory compliance ensures optimal performance while maintaining workplace safety. The proven technology’s decades of successful industrial service, combined with ongoing innovation, positions electric hoist winches as essential equipment supporting productive, safe, and profitable operations across global industrial sectors.
Need Expert Guidance? If you have technical questions about electric hoist winch selection, capacity requirements, or application specifications, our engineering team offers complimentary technical consultation services. Contact us anytime for free technical consultation and professional product quotations tailored to your specific lifting needs and operational conditions.
Technical Information Disclaimer
The specifications, performance data, and technical information presented in this guide are provided for general educational purposes only. All load capacities, operational parameters, and application recommendations represent typical industry values and may vary significantly between manufacturers, models, and specific configurations. Actual equipment performance depends on installation quality, operating conditions, maintenance practices, environmental factors, and proper operational procedures.
This guide does not constitute engineering specifications, safety recommendations, or purchasing advice. Organizations implementing electric hoist winch systems should:
- Consult qualified professional engineers for proper load calculations, structural adequacy verification, and safety factor determination
- Obtain detailed manufacturer specifications for specific models under consideration including certified load test documentation
- Verify regulatory compliance ensuring equipment meets applicable OSHA, ASME, CE, ATEX, and local jurisdiction requirements
- Implement comprehensive operator training programs meeting regulatory requirements and manufacturer recommendations
- Follow manufacturer installation and maintenance guidelines ensuring safe, reliable operation throughout equipment service life
No warranty is provided regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of information for any particular application. Equipment selection, installation, operation, inspection, and maintenance must occur under guidance of qualified professionals familiar with specific requirements, applicable regulations, and recognized industry standards.
For accurate, application-specific information and professional quotations, please contact certified electric hoist winch manufacturers, authorized distributors, or qualified material handling consultants who can evaluate your unique requirements and provide appropriate technical recommendations and safety guidance.
This disclaimer applies to all technical specifications, performance claims, application examples, safety information, and operational guidance presented throughout this document.



